Understanding Injection Molded Parts
What are Injection Molded Parts?
Injection molded parts are products manufactured using the injection molding process, a highly efficient and versatile technique that allows for the creation of complex shapes and designs. This process involves injecting molten material, typically thermoplastics or thermosets, into a pre-designed mold to form items that meet specified dimensions and properties. The result is a high-quality, repeatable part that can be produced at scale, catering to various industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods. Injection molded parts can include anything from simple plastic components like bottle caps to intricate assemblies such as housing for electronics.
Benefits of Injection Molded Parts
The advantages of using injection molded parts are plentiful. Some of the most significant benefits include:
- Cost Efficiency: Injection molding is an economical process, especially for mass production. The initial investment in molds can be high, but the cost per unit decreases significantly with larger production runs.
- High Precision: Injection molded parts are known for their accuracy, meaning that detailed designs can be achieved without compromising on quality.
- Design Flexibility: The injection molding process allows for a wide variety of materials and finishes, providing ample choices for designers.
- Less Waste: The precision of the process means that there is minimal waste material generated, making it a more environmentally friendly option compared to other manufacturing methods.
- Rapid Production: Once the mold is created, parts can be produced quickly, making it ideal for industries that require fast turnaround times.
Common Applications of Injection Molded Parts
Injection molded parts are ubiquitous in modern manufacturing and can be found in numerous applications, such as:
- Consumer Products: Items like containers, toys, and household products.
- Automotive Components: Dashboard panels, trims, and various internal parts.
- Electronics: Enclosures for devices such as smartphones and gaming consoles.
- Medical Devices: Syringes, surgical tools, and housings for various equipment.
- Industrial Equipment: Components used in machinery and assembly lines.
The Injection Molding Process Explained
Stages of Injection Molding
The injection molding process can be broken down into several critical stages:
- Material Preparation: The raw plastic material is often in pellet form and is heated until it melts.
- Injection: The molten plastic is injected into the mold at high pressure.
- Cooling: The plastic cools and solidifies inside the mold.
- Ejection: Once the part is cooled, it is ejected from the mold, and the process can begin again.
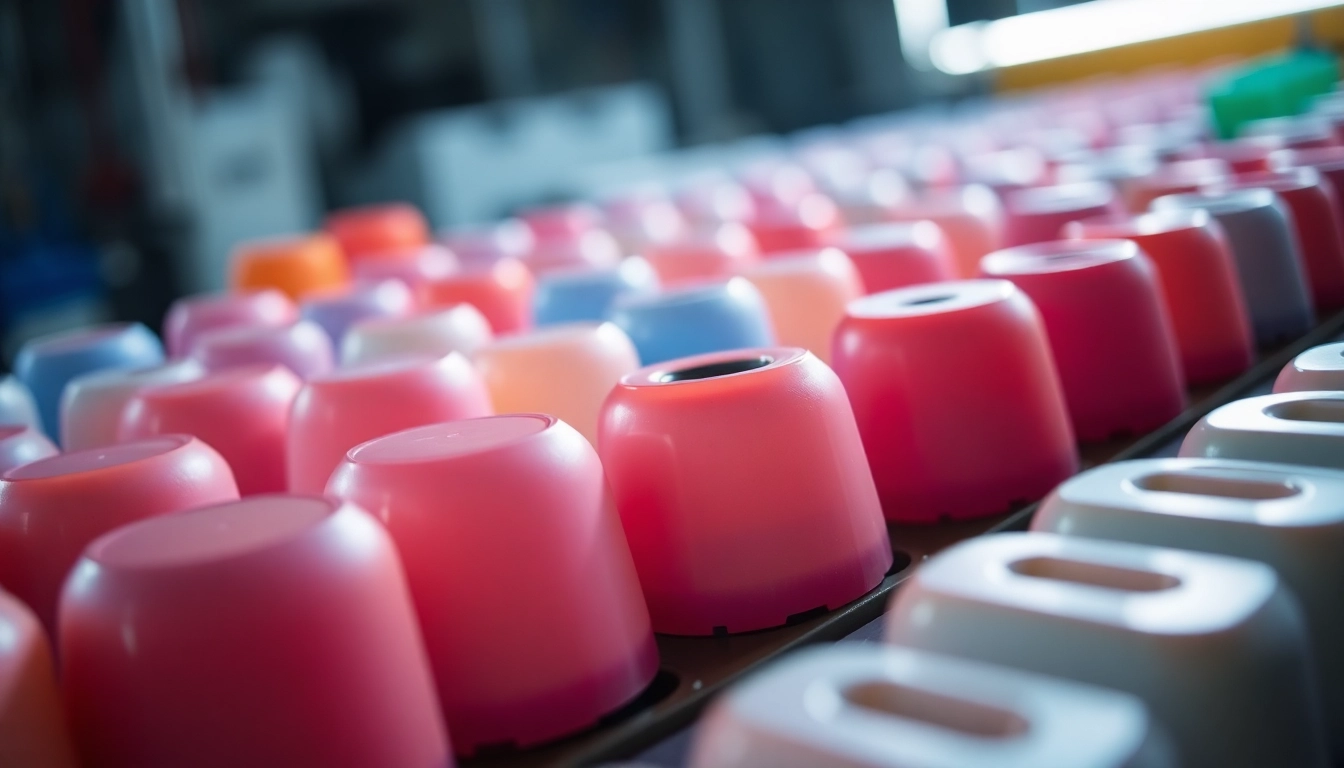
Materials Used in Injection Molding
Various materials can be utilized in injection molding, each with its own set of properties that make it suitable for different applications:
- Thermoplastics: Such as ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon, which can be heated and reshaped multiple times.
- Thermosetting Plastics: Such as epoxy and phenolic resins, which harden permanently after curing.
- Elastomers: Rubber-like materials that provide flexibility and resilience.
Quality Control in Injection Molding
Quality control is essential throughout the injection molding process to ensure that the final parts meet the desired specifications. This may include:
- Inspection: Visual and dimensional checks at various stages to ensure parts are within tolerance.
- Testing: Mechanical and thermal testing to ensure performance properties are met.
- Process Monitoring: Utilizing sensors and software to monitor the injection molding process in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments to maintain quality.
Designing Injection Molded Parts
Best Practices for Designing Effective Parts
Effective design of injection molded parts involves several best practices, including:
- Draft Angles: Incorporating draft angles to facilitate easy removal from the mold.
- Uniform Wall Thickness: Designing with consistent wall thickness to ensure even cooling and minimize warping.
- Minimizing Undercuts: Reducing or avoiding undercuts in the design can simplify the mold and reduce manufacturing costs.
- Simulation and Prototyping: Using CAD software and prototyping to test and visualize the design before production.
Factors Influencing Design Choices
Design choices can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Material Properties: Different materials can behave differently under heat and pressure, affecting the final design.
- Functional Requirements: The intended use of the part dictates its strength, flexibility, and durability.
- Manufacturing Constraints: Limitations of the injection molding process itself can impact how complex a design can be.
Case Studies of Successful Designs
Many companies have thrived by leveraging innovative designs through injection molding. For instance, consider the case of a prominent consumer goods company that re-engineered its packaging using injection molded parts. By shifting to a more ergonomic design, they not only improved user experience but also reduced material usage, leading to significant cost savings and enhanced sustainability.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting
Estimating Costs for Injection Molded Parts
Estimating costs for injection molded parts involves understanding several key components:
- Tooling Costs: The primary cost factor involves the creation of the mold. Depending on the complexity, this can be significant.
- Material Costs: The type of plastic used impacts per-unit cost and must be factored into the total budget.
- Production Volume: Higher volumes typically lead to lower costs per unit due to economies of scale.
Ways to Reduce Costs without Sacrificing Quality
There are several strategies manufacturers can adopt to reduce costs while maintaining quality, including:
- Optimization of Design: Streamlining part designs to minimize material use and complexity can result in cost savings.
- Strategic Material Selection: Choosing cost-effective materials that meet necessary performance criteria can also lower expenses.
- Efficient Production Processes: Implementing lean manufacturing principles can minimize waste and reduce overall production costs.
ROI of Investing in Quality Injection Molded Parts
Investing in high-quality injection molded parts can yield significant returns on investment. They often enhance product durability, reduce the need for replacement, and improve customer satisfaction. Moreover, by using quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques, businesses can differentiate themselves in the market, potentially leading to increased sales and customer loyalty.
Future Trends in Injection Molded Parts Manufacturing
Impact of Technology on Injection Molding
The landscape of injection molding is evolving rapidly due to advancements in technology. Innovations such as 3D printing for prototyping, AI-driven process optimization, and smart manufacturing technologies are transforming how injection molded parts are designed and produced. As these technologies continue to develop, they will enhance efficiency, reduce lead times, and improve customization capabilities.
Sustainability in Injection Molded Part Production
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, the injection molding industry is moving towards more sustainable practices. This includes:
- Recycling of Materials: Utilizing recycled plastics in the injection molding process can significantly reduce environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency: Innovations in machinery are allowing manufacturers to reduce energy consumption during production.
- Eco-friendly Designs: Designing parts with an emphasis on sustainability can appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
The Future of Customization in Injection Molding
Customization is becoming increasingly vital in various industries. The rise of digital technologies enables more companies to produce low-volumes of customized injection molded parts without prohibitive costs. As customization becomes more accessible, businesses will find new ways to meet individual customer needs, thus promoting greater innovation and diversity within the injection molded parts market.